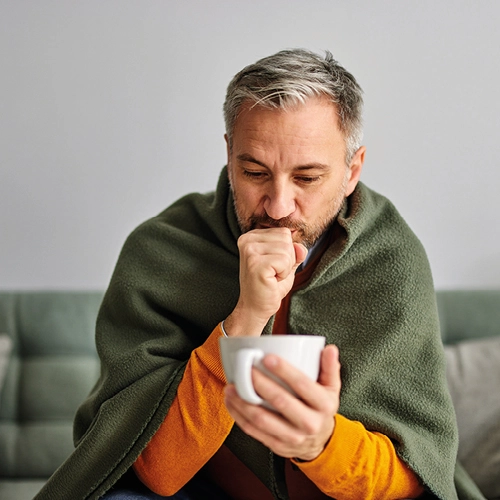
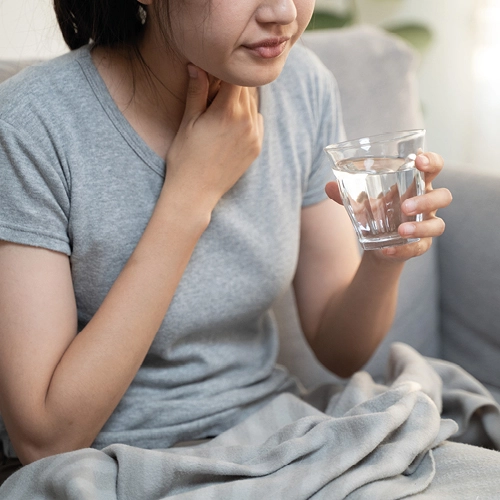
What are the symptoms of the flu?
The flu is caused by influenza viruses 1. Once tiny droplets of the virus have made their way into the body, your immune system gets activated — it starts making antibodies to fight off the viral intruder 1. But for that, it needs time 1. While your body fights off the virus, you may experience the following symptoms 1, 2, 3:
- A fever of 38°C–40°C (about 100–104°F) or above
- Chills
- Muscle pain
- Joint pain
- Headache
- Extreme tiredness or fatigue
- A general feeling of being very unwell (also called malaise)
- Cough
- Stuffy and/or runny nose
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting or diarrhoea (rarely and usually in children)
It’s best to consult your physician about your flu symptoms or if you’re worried about having the flu 1. A very high fever, especially in children, can be a cause for concern, and you should seek medical attention 4.
Flu vs. Cold Symptoms. Do you know the difference?
There are four main differences between a cold and the flu.
- The clue is in the name — the “common cold” occurs far more frequently than the flu 1.
- Colds and flu evolve quite differently: colds tend to start gradually, whereas the flu can hit you quite hard very suddenly 1.
- The flu tends to affect the entire body, whereas the common cold tends to affect just the airways that help you breathe 1.
- The flu is caused by influenza viruses 1. Common colds are caused by many different viruses 5.
Telling the difference between cold and flu symptoms can sometimes be confusing because colds and flus do share some common symptoms 1.
The table below shows the similarities and differences between cold and flu symptoms 5. It also shows how frequently these symptoms occur in each condition.
| Symptoms | Cold | Flu |
| Fever | Rarely | Almost aways |
| Tiredness or fatigue | Sometimes | Almost aways |
| Cough | Often | Almost aways |
| Sneezing | Almost aways | Never |
| Joint pain | Almost aways | Almost aways |
| Runny or stuffy nose | Almost aways | Almost aways |
| Sore throat | Almost aways | Almost aways |
| Diarrhea | Never | Sometimes in children |
| Headache | Sometimes | Almost aways |
| Loss of sense of smell or taste | Rarely | Rarely |
Source: Common colds: Overview - InformedHealth.org - NCBI Bookshelf 5.
How long do flu symptoms last?
Most people recover from their flu symptoms in less than 7 days 1, 3. However, other symptoms, such as cough and extreme tiredness can last up to 2 weeks 1, 2, 3. Full recovery from the flu can take longer than 2 weeks in older people or people with conditions such as chronic lung disease 3.
While most people recover swiftly from the flu, some can develop complications 2, 3. These complications can range from moderate to severe and could include:
- Sinus and ear infections
- Dehydration
- Pneumonia
Very rarely, and in very severe cases, the flu can become fatal 6. Very young children and older adults are at increased risk of complications 6. Other rare, severe complications could include:
- Inflammation of the heart
- Brain inflammation
- Muscle inflammation
- Kidney failure
- Respiratory failure
- Sepsis
People with other health problems should be aware that the flu can worsen their condition 2. For example, if you have asthma, heart disease, or diabetes, the flu can make it worse 2.
What is the treatment for the flu?
There are treatments for the flu that target the influenza virus. These are called antivirals 6, 7. However, most people don’t need them. In most cases, the flu goes away on its own 6.
There are some natural and home remedies that have been anecdotally used to relieve flu symptoms; however, there is no hard scientific evidence proving these remedies make the flu go away faster 1. These include:
- Drinking hot teas or other hot drinks to soothe your throat 1
- Having chicken broth to relieve congestion in your throat and nose 1
- Taking honey to soothe your cough 5
- Drinking plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration 1
While you’re ill, it’s important that you stay at home to avoid passing on the virus to other people 7. If you need to leave the house for medical care, avoid spreading the virus by washing your hands frequently and throwing away used tissues 1. You can also learn how to stop a coughing fit in public.
When to see a doctor
People who are otherwise healthy, have no other chronic conditions, and experience a mild case of the flu do not usually need treatment, beyond symptoms relief 6.
However, if you’re worried about your symptoms, or if you are at an increased risk of complications from the flu, make an appointment with your doctor 1, 7. Complications can happen to anyone but people at higher risk of flu complications are 2:
- Young children
- Adults over the age of 65
- Pregnant people
- People with chronic health conditions
Finally, some flu symptoms overlap with those of COVID-19. Read on to find out the difference between the flu and COVID.
FAQs
- Diarrhea
- Tummy pain or cramps
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever (occasionally)
- People with lung disease
- People with diabetes
- People with other chronic illnesses
- Adults older than 65
- Children
- Fever
- Muscle pain
- Joint pain
- Tiredness
- Headache
- Pain, redness, or swelling where the injection was made
- Your fever is over 40°C (104°F)
- You still have a fever after 3 days despite home remedies or treatments
- You are shivering and shaking uncontrollably
- Your condition is getting worse rather than better
- You have a severe headache
- You have any other unusual symptoms such as increased heart rate, hallucinations, vomiting, etc.
What people commonly refer to as “stomach flu” is actually a condition called viral gastroenteritis 8. Influenza (flu) and gastroenteritis (“stomach flu”) are different 9. Flu viruses affect the respiratory system, while the viruses that cause gastroenteritis affect the intestines 9. Flu viruses cannot cause “stomach flu”9.
Stomach flu symptoms include 9:
Some studies estimate that in healthy adults, the flu shot is 60% effective 10.
Although the flu vaccine is not 100% effective, it reduces the intensity of the symptoms and the time that you are ill 6. It also prevents hospitalization in 6:
The flu shot may cause some side effects, which can resemble the symptoms of a flu 9. These flu-like symptoms are 10:
Yes, it is possible for stress to cause some flu symptoms. However, the mechanisms by which this happens are not entirely clear 11, 12. Some of the flu-like symptoms that stress can cause are
Some research has found that people who have gone through majorly stressful life events are more vulnerable to developing a cold when they are exposed to a virus 12. Your immune system is there to protect you, but stress may sometimes cause an inflammatory response that keeps your immune system from doing its job properly 12.
For some people, stress-induced fever can go as high as 41°C (105.8°F) 11.
Fever is defined as a body temperature of 38°C (100.4°F) or above 13. High fever is 39.5°C (103.1°F) or higher, and very high fever is anything above 41°C (105.8°F) 13.
A high fever can be a cause for concern, and a very high fever can be dangerous 4.
Speak to your doctor if you are concerned about your fever, particularly about fever in your child 4. if your child has even mild fever but is 6 months or younger, you should speak to a medical professional 4.
You should also seek medical attention if 4:

1. InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. Flu: Overview. 2013 Dec 18 [Updated 2019 Nov 7]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279459/
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Flu Symptoms & Complications, accessed 29/09/2022, available at https://www.cdc.gov/flu/signs-symptoms/index.html
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Clinical Signs and Symptoms of Influenza, accessed 29/09/2022, available here https://www.cdc.gov/flu/professionals/acip/clinical.htm
4. Better Health Channel, Fever, accessed 29/09/2022, available at https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/fever
5. InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. Common colds: Overview. [Updated 2020 Oct 8]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279543/
6. Boktor SW, Hafner JW. Influenza. [Updated 2022 Jul 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459363/
7. CDC, Flu: What To Do If You Get Sick, accessed 29/09/2022, available here https://www.cdc.gov/flu/treatment/index.html
8. What are the symptoms of Omicron?, ZOE Editorial Staff, ZOE app, accessed 24/10/2022, available here https://joinzoe.com/learn/omicron-symptoms
9. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), Symptoms & Causes of Viral Gastroenteritis (“Stomach Flu”), accessed 07/10/2022, available here https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/viral-gastroenteritis/symptoms-causes
10. Informed Health, How much protection do flu vaccinations offer?, accessed 29/09/2022, available here https://www.informedhealth.org/how-much-protection-do-flu-vaccinations-offer.html
11. Oka T. Psychogenic fever: how psychological stress affects body temperature in the clinical population. Temperature (Austin). 2015 Jun 3;2(3):368-78. doi: 10.1080/23328940.2015.1056907. PMID: 27227051; PMCID: PMC4843908.
12. Cohen S, Janicki-Deverts D, Doyle WJ, Miller GE, Frank E, Rabin BS, Turner RB. Chronic stress, glucocorticoid receptor resistance, inflammation, and disease risk. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Apr 17;109(16):5995-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1118355109. Epub 2012 Apr 2. PMID: 22474371; PMCID: PMC3341031.
13. InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. How is body temperature regulated and what is fever? 2009 Jul 30 [Updated 2016 Nov 17]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279457/
a. Mucosolvan Syrup leaflet last revised in July 2022.
b. Mucosolvan 75mg capsules leaflet last revised in July 2022.
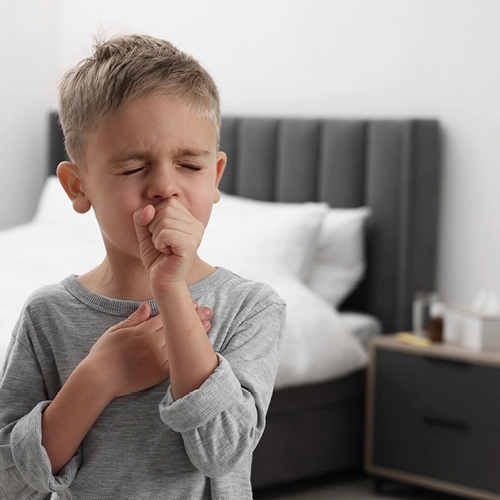


%20(1)%20(1).webp)

-2.webp)
%20(1).webp)
%20(1).webp)
